netter76
Airway Struclure: Trachea and Major Bronchi
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
Thyroid cartilage -Cricothyroid ligament -Cricoid cartilage-
Connective tissue sheath Cartilage
Elastic fibers Gland
Smali artery
Lymph ves$el$ Nerve
pithelium
Connective tissue sheath <cut away)
Cross section through trachea
Postcrior wali
Tracheal cartilages
Mucosa showing longitudinal folds tormcd by dense collections of elastic fibers
Epartcrial
bronchus
Nerve
Smali arteries | Gland
| Tachealis musde Esophageal musde Epithelium
Elastic fibers Lymph vessels
uppcr
lobe
To
middle
lobe
bronchus bronchus
Intrapulmonary Extrapulmonary
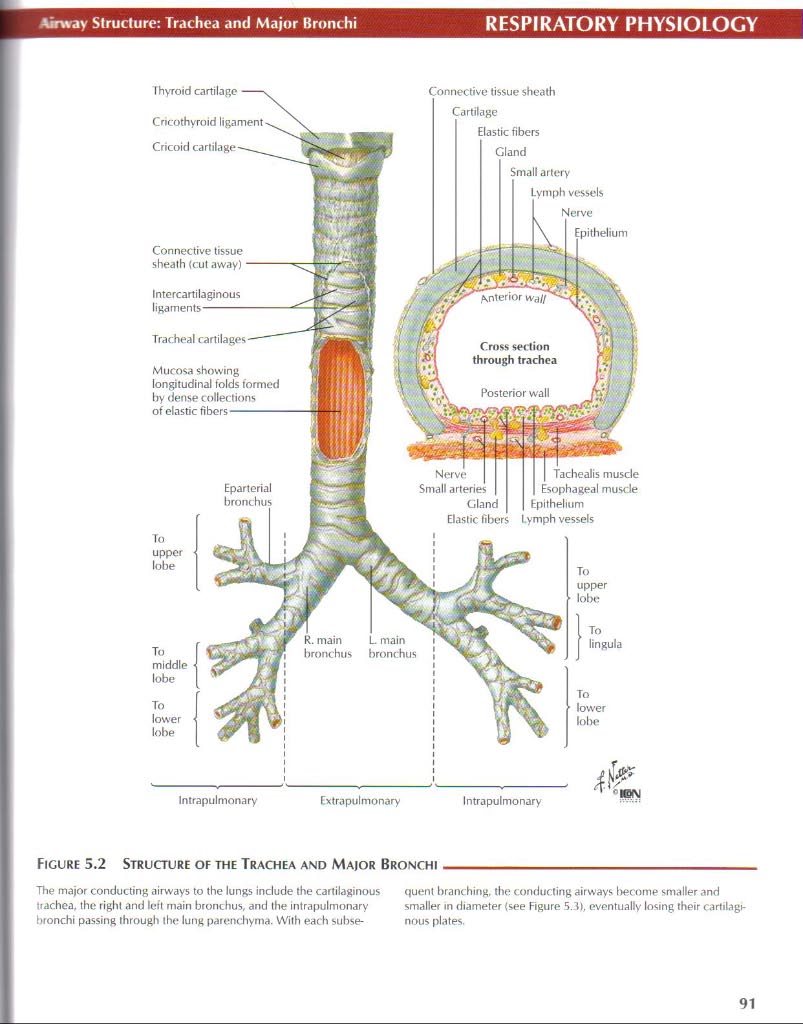
Figurę 5.2 Structure of the Trachea and Major Bronchi
The major conducting airways to the lungs indude the cartilaginous tiachea, the right and Icft main bronchus, and the intrapulmonary bronchi passing through the lung parenchyma. Wilh each subse-quent branching, the conducting airways become smaller and smaller in diameter <see Figurę 5.3), eventually losing their cartilagi-nous plates.
91
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter128 Autonomie and Enteric IntegrationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY AUTONOMIC NERYOUS SYSTEM SYMP
netter143 Rectum and Anal CanalGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Sigmoid colon Rectosigmoid junction Super
netter78 Airway Structure: EpithcliumRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Mucus- Goblet (mucous)
netter93 O, and CO_. ExchangrRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 5.19 02 and CO, Exchange As blood flows I
57225 netter117 Potassium ExcretionRENAL PHYSIOLOGY Low K’ Diet Normal and High K*
netter120 ienal Produclion of New HCO,RENAL PHYSIOLOGY NH4A - acid Net Acid txcretion(NAE)«(UuxV) -
netter82 Nłedianics of Respiration: Elastic Properties IRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY During a slow expirat
F00574 019 f024 High-dose inhaled corticosteroids and regular bronchodilators Occasional temporary s
więcej podobnych podstron