99 (123)
6.8. IB. Therapy for the iliopsoas. Maximal stretching.
Starting Position: P: Prone; trunk in left lateral flexion; left leg over side of couch with foot on floor; to avoid lumbar lordosis (which may be painful). foot may be moved forward on the floor and stabilized in position by T's left foot; this flexes hip further, flattens the lordosis and prevents P evading the stretching; left foot position regulates lumbar lordosis, important in treating patients with Iow back pain; a cushion may be placed under the abdomen to increase ventral flexion of the lumbar spine (and therefore the effect of the stretching); pelvis stabilized with a belt; right knee flexed with right hip in fuli medial rotation. T: Standing obliąue, facing Ps left side level with P’s thighs.
Grip: T’s right hand grips P's lower leg just above the ankle. After raising lower end of couch (see Procedurę), Ts left hand can be used to stabilize P’s right thigh at the dorsal side just distal to the ischial tuberosity; this increases stretching.
Procedurę: Using this grip, T uses left hand to slowly raise the foot end of the couch, thereby gradually and fully extending medially rotated hip.
Stimulation of Antagonists: T moves right hand to dorsal side of thigh just proximal to knee. T then asks P to move further in the direction of stretching, and resists that movement to stimulate P’s antagonists. To increase contraction when stimulating, T uses left hand to slap P’s right buttock.
Notę: If the belt stabilization fails to hołd P's pelvis in place after the foot end of the couch is raised, T’s left hand can be placed over P’s right thigh to press the pelvis ventrally towards the couch.

Fig. 73 a. Starting Position.
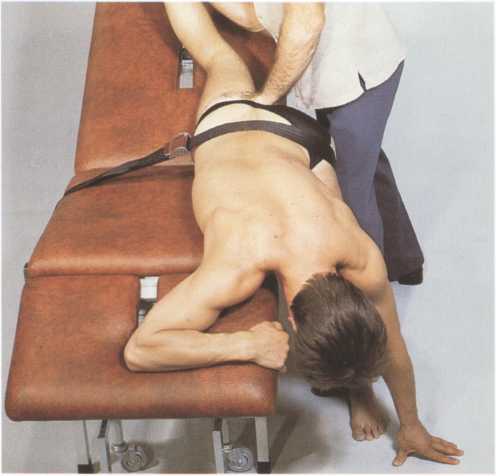
Fig. 73 b. Finał Position.
102
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
58 (288) 3.3.8. Therapy for the extensor digiti minimi. Starting Position: P: Supine; arm flexed app
60 (279) 3.3.10. Therapy for the extensor carpi ulnaris. Starting Position: P: Supine; arm flexed ap
61 (266) 3.3.11. Therapy for the flexor carpi ulnaris. Starting Position: P: Supine; arm flexed appr
62 (264) 3.3.12. Therapy for the flexor carpi radialis. Starting Position: P: Supine; arm flexed app
69 (223) 4.2.1. Therapy for the extensor pollicis longus. Starting Position: P: Supine; upper arm an
71 (222) Therapy for the flexor pollicis longus. Starting Position: P: Supine; upper arm and elbow r
73 (202) 4.5.1. Therapy for the abductor pollicis longus. Starting Position: P: Su
74 (201) 4.5.2. Therapy for the extensor pollicis brevis. Starting Position: P: Supine or sitting; e
29 (669) 2.3.1. Therapy for the deltoid, spinał part. Starting Position: P: Supine; knees and hips f
32 (618) 1 2.3.4. Therapy for the trapezius, transverse part. Starting Position: P: Lying on left si
80 (192) 5.3.1 Therapy for the flexor pollicis brevis. Starting Position: P: Supine or sitting; elbo
86 (164) 5.9.1. Therapy for the opponens digiti minimi. Starting Position: P: Supine or sitting; elb
45 (422) 2.12.2A. Therapy for the levator scapulae. SHH Starting Position: P: Supine; head and neck
55 (319) 3.3.5. Therapy for the extensor digitorum communis. Starting Position: P: Supine; arm flexe
37 (438) 2.8.1. Therapy for the trapezius, ascending part. Starting Position: P: Lying on left side;
79 (188) 3.10. IB. Therapy for the sternocleidomas-toideus. Moderately shortened muscle. Starting Po
98 (127) 6.8.1A. Therapy for the iliopsoas. Muscle markedly shortened. Starting Position: P: Prone w
77 (196) 5.2.1. Therapy for the interossei dorsales. (Stretching of interosseus dorsalis I shown) St
78 (191) 5.2.2. Therapy for the interossei palmares. (Stretching of interosseus palmaris IV shown.)
więcej podobnych podstron