netter4
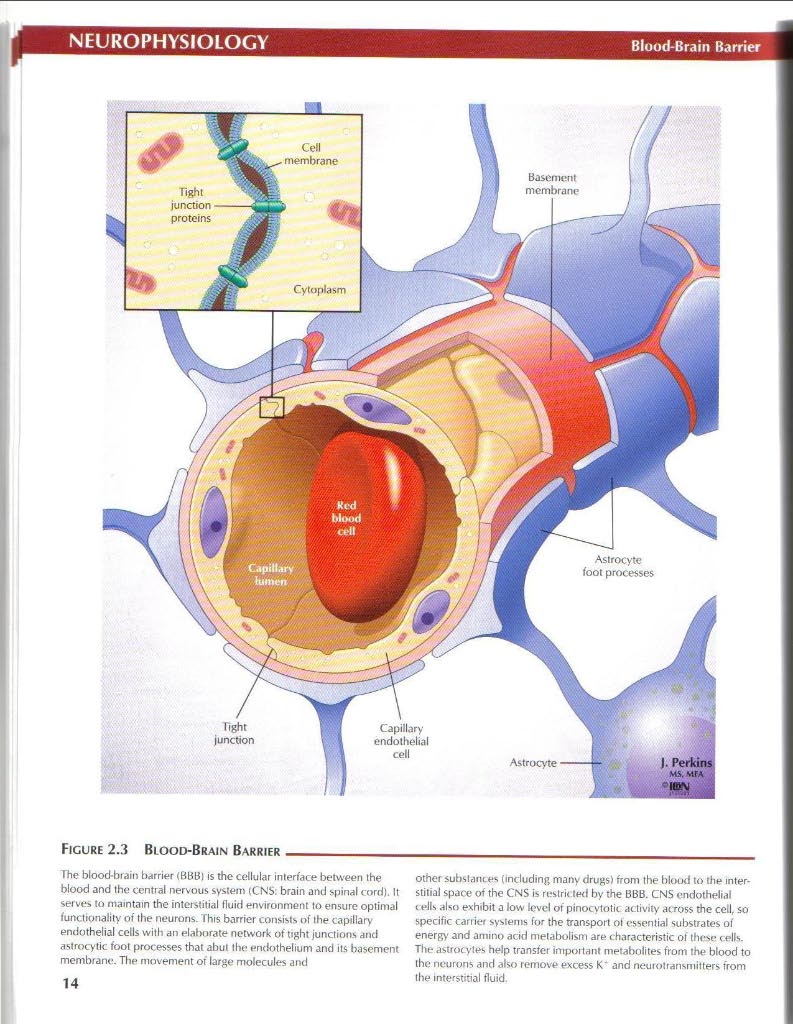
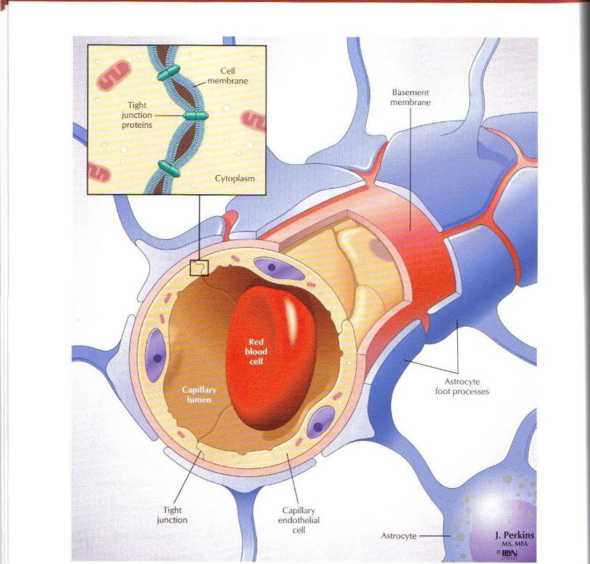
Figurę 2.3 Biood-Brain Barrier_
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the cełlular interface between ihe blood and the central nervous system (CNS: brain and spinał cord). It serves to maintain the interstitial fluid environment to ensure optimal functipnałity oi the neurons. This barrier consists c»f the capillary endothelial cells with an elaborate network ot tight junctions and astrocytic foot processes that abut the endothelium and its basement membranę. The nuwement ot large molecules and other subslam.es (induding many drugs) from the blood to the interstitial space ot the CNS is restrit ted by the BBB. CNS endothelial t eJls also exhibit a Iow k?vel ot pinocytotic activity across the celi, so specific carrier Systems for the transport ol essential substrates of energy and amino acid melabolism are characteristic of thesc cells. The astrocytes help transfer intportant metabolites from the blood to the neurons and also remove excess K' and neurotransmilters from the interstitial fluid.
14
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter11 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition Frontal (ant
netter2 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Central sulcus (Rotando)Organizalion of Ihe Brain: Cerebrum Postcentral gyru
30499 netter3 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYOn>anization of the Brain: Celi Types Multipolar (pyramidal) celi of
47720 netter8 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Inhibitory Mechanisms Figurę 2.7 Synaptic Inhibi
netter34 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYVisual Syslem: Visu.il Palhway Figurę 2.33 Retinoceniculostriate Visuai Paih
netter38 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYVcstibular System: Vestihulospin.il Tracts Figurę 2.37 Vestibulospinal Tract
netter10 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Tr.insmission: Temporal and Spatial Summation C. Icmporal exritator
netter126 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.5 Aijtonomic Innervation The inn
netter134 Castric DigestionGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.12 Gastric Digestiye Function The st
więcej podobnych podstron